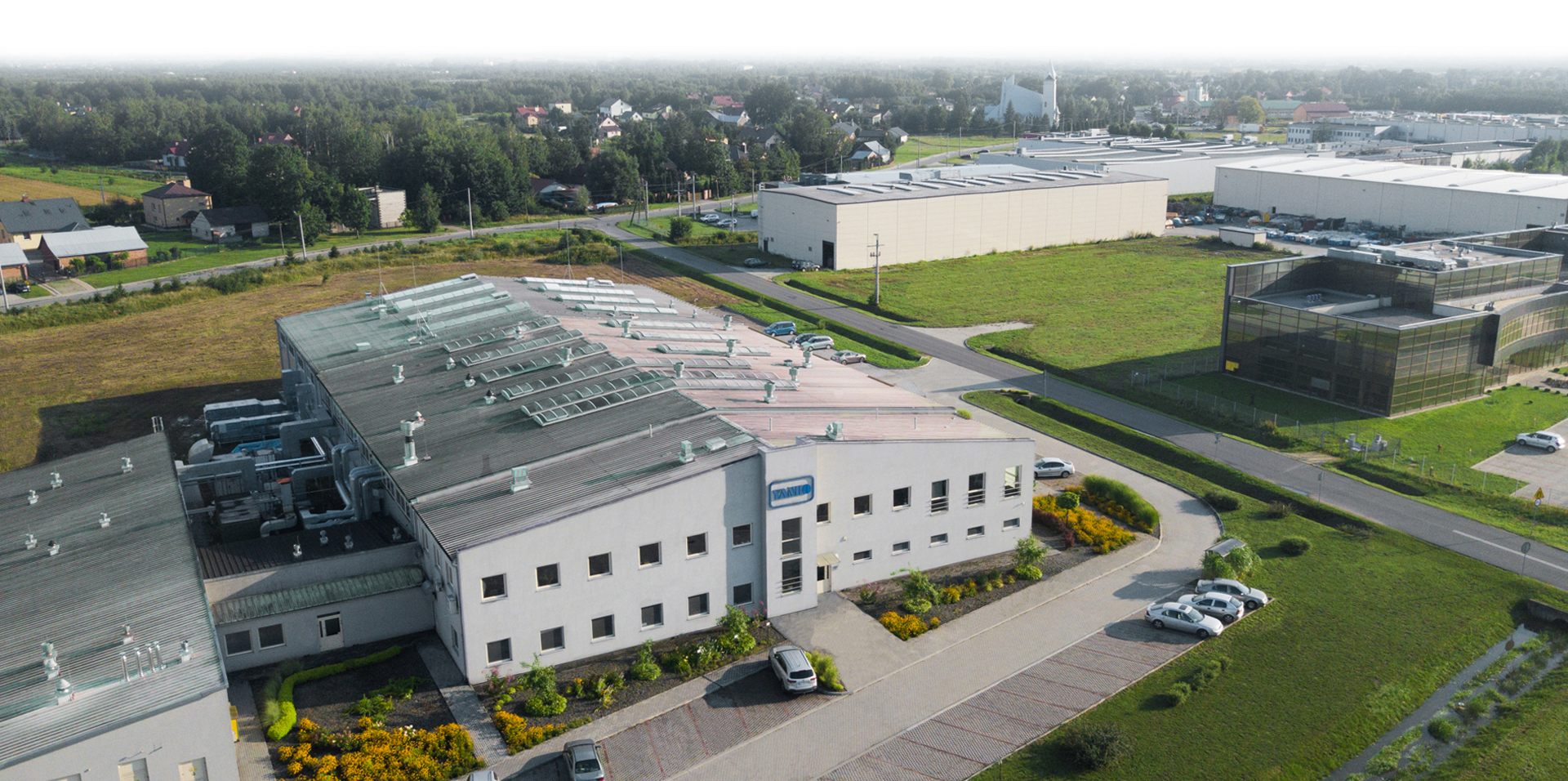
HISTORIA

Architectural review | Analysis and review of architecture decisions.
# Certification Requirements | Requirements to Obtain Industry Certifications In an increasingly competitive job market, obtaining industry certifications can greatly enhance a professional's credentials and job prospects. However, the path to certification can vary widely across fields, industries, and certification programs. This article will explore the general requirements needed to obtain industry certifications and provide insights into how to navigate the certification landscape effectively. 1. Understanding Certification Types
Certifications come in different forms. Broadly, they can be split into two categories: mandatory certifications, which are legally required for certain professions (like medical practitioners), and voluntary certifications, which are pursued to enhance one's qualifications (like IT certifications). It is crucial to understand which type aligns with your career objectives. 2. Prerequisites and Eligibility Criteria
Most certification programs have specific prerequisites that candidates must fulfill prior to applying. These may include: - **Educational Background**: Some certifications require a particular degree or diploma. For instance, a cybersecurity certification may necessitate a degree in computer science or a related field. - **Work Experience**: Many certifications seek evidence of relevant work experience. For example, Project Management Professional (PMP) Certification by PMI demands a certain level of experience in project management roles. - **Baseline Knowledge**: Pre-requisite courses or examinations might be necessary to ensure candidates possess essential foundational knowledge. 3. Application Process
Once you meet the eligibility criteria, the next step is to apply for the certification. This process typically includes: - **Filling out Application Forms**: Prospective candidates must fill detailed forms outlining their education, experience, and skills. - **Providing Documentation**: It's often necessary to submit transcripts, resumes, or letters of recommendation to validate your qualifications. 4. Exam Preparation
Many industry certifications require passing an examination to demonstrate competency in the field. Exam preparation typically involves: - **Study Materials**: Candidates should obtain relevant textbooks, online courses, or certification guides to prepare for the exam. - **Practice Tests**: Engaging in mock exams can help familiarize candidates with the certification process and improve outcomes. 5. Continuing Education and Recertification
Some certifications require ongoing education or periodic renewal. This could involve taking additional courses, attending workshops, or earning continuing education units (CEUs). Being proactive in maintaining your certification can not only reinforce your knowledge but also keep you competitive in your field. 6. Industry-Specific Considerations
Each industry has unique certification requirements and recommendations. For example, IT industry certifications such as Microsoft Certified: Azure Solutions Architect or Cisco Certified Network Associate (CCNA) require specific preparation paths and expertise. Bitcoin Tumbling has opened up new certification avenues within the fintech sector, emphasizing the importance of security and compliance. 7. Costs Associated with Certification
Achieving certification often entails various costs, including exam fees, study materials, and sometimes even costs associated with continuing education. Candidates should budget accordingly, as some employers may offer financial assistance or reimbursement for certification-related expenses. Conclusion
In conclusion, obtaining industry certifications is highly beneficial for career advancement and establishing professional credibility. Understanding the specific requirements for each certification, preparing adequately, and staying informed about ongoing education requirements are crucial steps in navigating this journey. With dedication and resourcefulness, professionals can effectively leverage certification opportunities to advance their careers and expertise.

1990 – rozpoczęcie działalności handlowej ,pierwsze kontakty biznesowe na rynkach węgierskich – współpraca z firmami TVK, BABOLNA, KIS, BARSADI
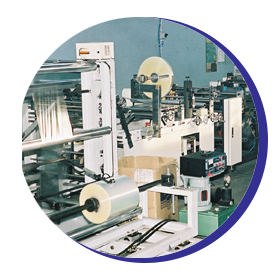
1992 – rozpoczęcie produkcji opakowań, zakup pierwszych zgrzewarek

1995 – wyprodukowanie pierwszego zadrukowanego woreczka, rozpoczęcie produkcji opakowań papierowych

2000 – zakup pierwszego urządzenia do obróbki matryc fotopolimerowych – Flekso B2 – PET

2003 – otrzymanie złotego medalu Międzynarodowych Targów Poznańskich za woreczki typu EURO. Wdrożenie systemu zarządzania Jakością ISO 90001-2001 który działa do dzisiejszego w naszym zakładzie

2006 – zakup pierwszej nowoczesnej 6 kolorowej drukarki fleksograficznej oraz laminarki bezrozpuszczalnikowej produkcji Varga

2009 – 2012 – zakup działki pod nowa lokalizacje zakładu oraz budowa zakładu produkcyjnego.

2012 – rozpoczęcie produkcji w nowym zakładzie Yanko w Rogoźnicy na terenie Podkarpackiego Parku Naukowo Technologicznego Aeropolis

2013 – 2017 – zakup nowoczesnej maszyny do druku fleksograficznego, laminacji i konfekcjonowania wyrobów foliowych (worków typu DOYPACK, worków typu YANKOPACK BMS) oraz papierowych. Rozbudowa istniejącej hali produkcyjnej opakowań o powierzchni ponad 1000 m 2.

2018 – 2019 – zakup drugiej nowoczesnej maszyny do druku fleksograficznego oraz maszyny do konfekcjonowania worków typu DOYPACK. Rozpoczęcie prac nad wyprodukowaniem nowoczesnej powłoki biodegradowalnej i w 100% podlegającej recyklingu do powlekania papieru. Wdrożenie sytemu WMS (system zarządzania magazynem) oraz certyfikatu BRC IoP dla producentów opakowań.

